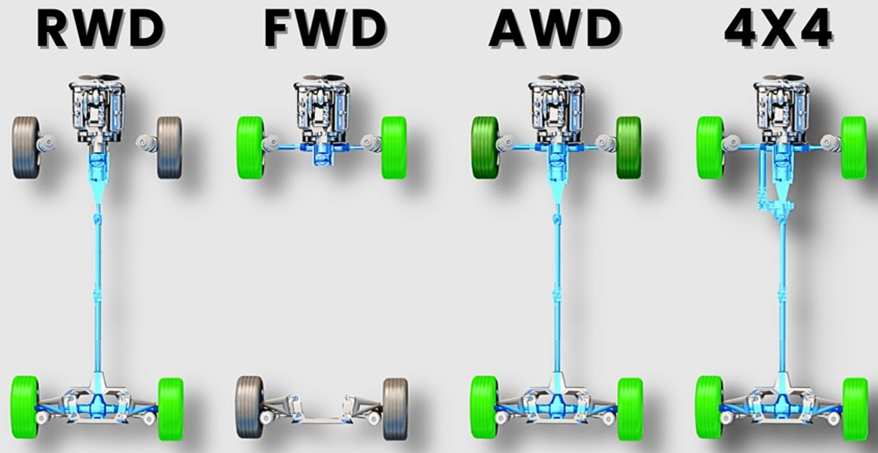
If you're in the market for a new vehicle, understanding these drivetrains could be the key to finding the perfect fit for your needs.
The world of drivetrains can seem complex, but understanding how each system works and what it offers is crucial when choosing your next vehicle.
From the dependable FWD found in many budget-friendly sedans to the rugged 4WD systems of off-road beasts, each setup serves a specific purpose. Let’s break down what you need to know.
FWD (Front-Wheel Drive)
Overview:
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) systems deliver power exclusively to the front wheels. It’s the most common drivetrain found in modern vehicles, especially compact cars, family sedans, and economy vehicles.
How It Works:
The engine’s power is transmitted to the front wheels, which both drive and steer the vehicle. This design simplifies manufacturing and reduces weight, making it a popular choice for fuel-efficient vehicles.
Advantages:
-
Affordability: Vehicles with FWD systems are generally less expensive to manufacture, leading to lower purchase prices.
-
Fuel Efficiency: With a lighter drivetrain, cars with FWD offer better fuel economy.
-
Improved Traction in Wet Conditions: The engine’s weight over the front wheels enhances traction on slick or rainy roads.
Disadvantages:
-
Understeer: Due to power being sent only to the front, FWD vehicles can struggle with cornering precision.
-
Limited Off-Road Capability: Poor performance on rough or slippery terrain.
Popular FWD Models:
-
Honda Civic (Starting at $23,000)
-
Toyota Camry (Starting at $27,000)
RWD (Rear-Wheel Drive)
Overview:
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) systems send power to the rear wheels, providing a sportier, more dynamic driving experience. Commonly found in sports cars, luxury sedans, and trucks.
How It Works:
The engine’s power is transmitted to the rear wheels, allowing the front wheels to focus entirely on steering. This setup often provides better balance and handling performance.
Advantages:
-
Better Handling: Enhanced balance and control, especially during high-speed maneuvers.
-
Superior Towing Ability: Often used in trucks for its ability to handle heavier loads.
-
Durability: Stronger drivetrains capable of handling more power.
Disadvantages:
-
Reduced Traction on Slippery Surfaces: Poor performance in rain, snow, or ice without assistance from traction control systems.
-
Higher Cost: Typically more expensive than FWD vehicles.
Popular RWD Models:
-
BMW 3 Series (Starting at $44,000)
-
Ford Mustang (Starting at $32,000)
AWD (All-Wheel Drive)
Overview:
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) provides power to all four wheels simultaneously, or automatically adjusts power distribution based on road conditions. It’s designed for enhanced control in various driving conditions.
How It Works:
AWD systems can be full-time or on-demand. Full-time AWD delivers continuous power to all wheels, while on-demand AWD activates only when additional traction is necessary.
Advantages:
-
Improved Traction: Excellent control on wet, snowy, or icy roads.
-
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of road conditions and light off-roading.
-
Enhanced Stability: Better handling in various weather conditions.
Disadvantages:
-
Lower Fuel Efficiency: Increased weight and complexity reduce overall fuel economy.
-
Higher Maintenance Costs: More complex systems can be expensive to repair.
Popular AWD Models:
-
Subaru Outback (Starting at $29,000)
-
Audi Q5 (Starting at $46,000)
4WD (Four-Wheel Drive)
Overview:
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) systems are built for off-road enthusiasts and heavy-duty performance. Designed primarily for rugged terrain, it’s the go-to choice for trucks and SUVs with off-road ambitions.
How It Works:
Unlike AWD, most 4WD systems are manually engaged by the driver. High-range and low-range settings allow the vehicle to tackle challenging environments like mud, sand, or steep inclines.
Advantages:
-
Maximum Traction: Unmatched performance in extreme off-road conditions.
-
Towing Capability: Ideal for pulling heavy loads over challenging terrains.
-
Durability: Built to withstand harsh conditions and heavy use.
Disadvantages:
-
Fuel Consumption: The heaviest and most inefficient drivetrain option.
-
Poor On-Road Handling: Not designed for precision handling on paved roads.
Popular 4WD Models:
-
Jeep Wrangler (Starting at $33,000)
-
Ford F-150 (Starting at $36,000)
Choosing the Right Drivetrain for You
Selecting the best drivetrain depends on your specific needs. Here’s a quick breakdown to help you decide:
-
FWD: Great for everyday driving, budget-conscious buyers, and city commutes.
-
RWD: Perfect for enthusiasts seeking enhanced performance and handling.
-
AWD: An excellent all-around option for those who regularly drive on wet, icy, or uneven surfaces.
-
4WD: The ultimate choice for off-road adventurers and heavy-duty tasks.
| Drivetrain | Ideal For | Price Range (Approx.) | Best Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| FWD | Everyday Commuting, City Driving | $23,000 – $30,000 | Honda Civic, Toyota Camry |
| RWD | Performance Enthusiasts, Towing | $32,000 – $44,000 | Ford Mustang, BMW 3 Series |
| AWD | All-Weather Driving, Versatility | $29,000 – $46,000 | Subaru Outback, Audi Q5 |
| 4WD | Off-Road Adventures, Heavy Towing | $33,000 – $36,000 | Jeep Wrangler, Ford F-150 |
As you consider your next vehicle, remember to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each system against your lifestyle, driving conditions, and budget. Now that you’re armed with the knowledge to make an informed decision, happy car shopping!